War with China: Are we closer than we think? | Under Investigation
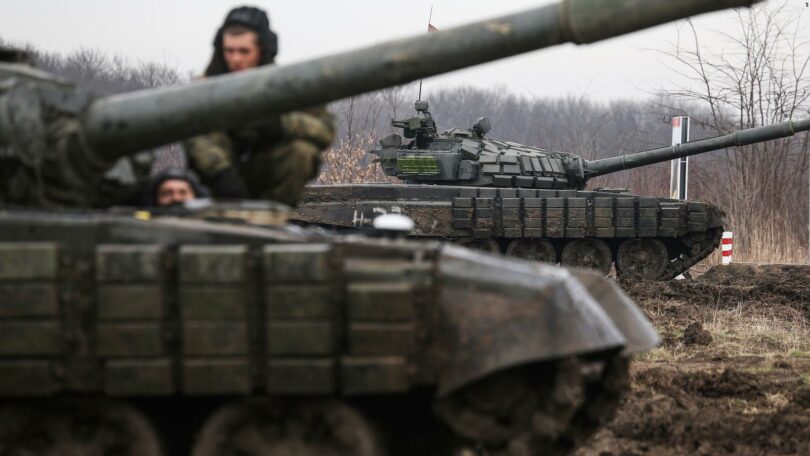

Fighting two wars at the same time
In the eyes of the U.S., China and Russia are the two most important adversaries: their vast territory, long history, profound national culture, and strategic nuclear weapons are all threats to American global hegemony. According to the U.S., the only way to eliminate the threat is that the two great powers’ submit to U.S.’ global hegemony. As regards Russia, which has yet to recover from its weakness, the U.S. hopes to completely dismantle it and destroy its nuclear weapons, causing it to lose all global influence. As regards China, which has a more united people, a more stable ruling party, and a healthier economy, the U.S. hopes to overthrow its leaders through a “color revolution” and gradually erode the Chinese people’s faith in communism. Maintaining military containment of both countries is, in Kroenig’s view, a non-negotiable premise.
00:00:00 - Could US Military Take on China (China vs United States - Who Would Win)
00:20:33 - What if China Launched an Attack on USA
00:41:12 - Why China is Terrified of US Airforce
01:03:38 - Why Russia’s Invasion of Ukraine is a Disaster for China
01:27:39 - This Is Why China Will Start WW3
01:47:37 - Who Are the Quad and Why Are They After China
02:07:42 - America's Plan to Checkmate China
02:27:35 - How The Philippines Is Ruining China's Plans To Conquer Taiwan
02:46:59 - How the Philippines Became Key to US Pacific Strategy
03:06:55 - China's Brand New Aircraft Carrier vs USS Gerald R. Ford Supercarrier
Another proposal is to include U.S. “key allies in military planning, sharing responsibilities, and streamlining the division of labor for weapons procurement”. With the U.S. and its formal treaty allies accounting for nearly 60% of global GDP, Kroenig suggests that the U.S. supplement existing alliances (e.g., NATO, bilateral alliances in Asia) with new arrangements like the Quadrilateral Security Dialogue (QUAD) to “more easily mobilize resources and maintain military superiority over China and Russia”. He suggested that U.S. European allies invest in armor and artillery, while Asian allies purchase mines, harpoon missiles, and submarines, and the U.S. Army prioritizes Europe while the U.S. Navy handles the Indo-Pacific.
The current U.S. policy towards Russia is not a blip on the radar, but a continuation of a decades-long Cold War strategy. In 1972, shortly after Kissinger’s secret visit to China, he told President Nixon that the Chinese were “just as dangerous as the Russians, and even more dangerous in certain historical periods”. He hoped that Washington could take advantage of Moscow and Beijing by playing “an unemotional balance of the power game”. In Kissinger’s view, 20 years later, the U.S. would lean towards Russia to restrain China, if it could first use China to weaken the Soviet Union. Subsequent U.S. administrations (both Democrat and Republican) followed through on this strategy, working with China and weakening the Soviet Union, hastening its collapse.
But the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991 did not fully satisfy the U.S. During Yeltsin’s administration, the U.S. failed to persuade Russia—like Ukraine, Belarus, and Kazakhstan—to give up its nuclear weapons altogether. After the U.S. withdrew from the 1972 ABM Treaty in 2001, Russia also withdrew from the START II Treaty. At this time, Russia still deployed more than 5,000 strategic nuclear warheads and maintained a strong influence in Eastern Europe. The goal of the U.S. is to further weaken or destroy Russia economically, destabilize its politics, confuse the Russian people, and eventually dismantle Russia into smaller countries, and most importantly, eliminate its nuclear arsenal.
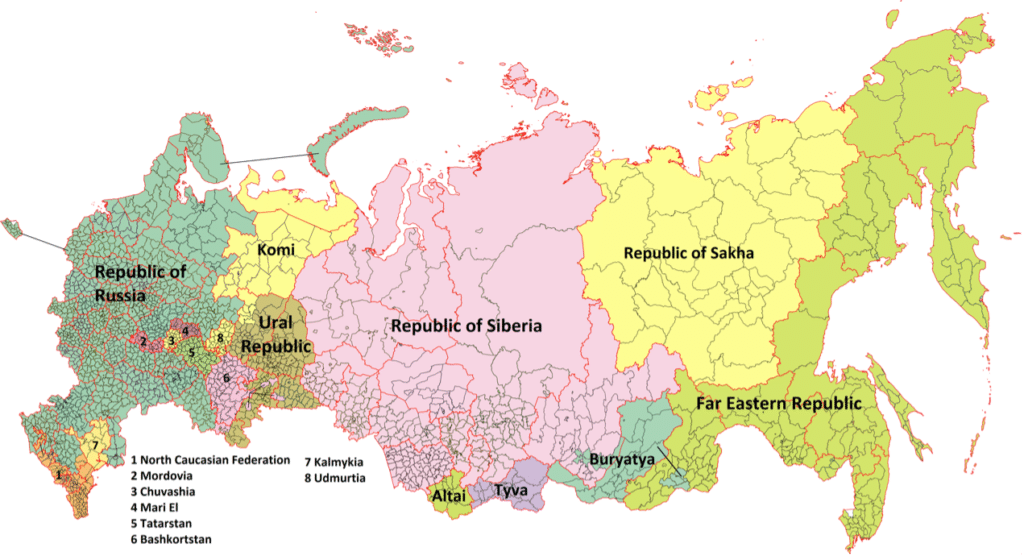
NATO’s eastward expansion has pushed the security issue in Ukraine to a boiling point. Prior to the collapse of the Soviet Union, the U.S. promised Mikhail Gorbachev that NATO would not expand eastward because its original mission—to confront the Soviet Union and contain communism in Europe—had come to an end when the Cold War ceased. However, NATO reneged on this “gentleman’s agreement” after the Cold War by adopting 14 more member countries, including some former members of the Soviet Union. In 2018, Ukraine amended its constitution to make attaining NATO and EU membership its primary national strategy, which posed a serious threat to Russia’s national security. As Kyiv, Ukraine’s capital, is only 760 kilometers in a straight line from Moscow, giving permission to NATO to deploy ultra-high-sonic nuclear weapons in Ukraine would almost certainly mean the total military surrender of Russia.
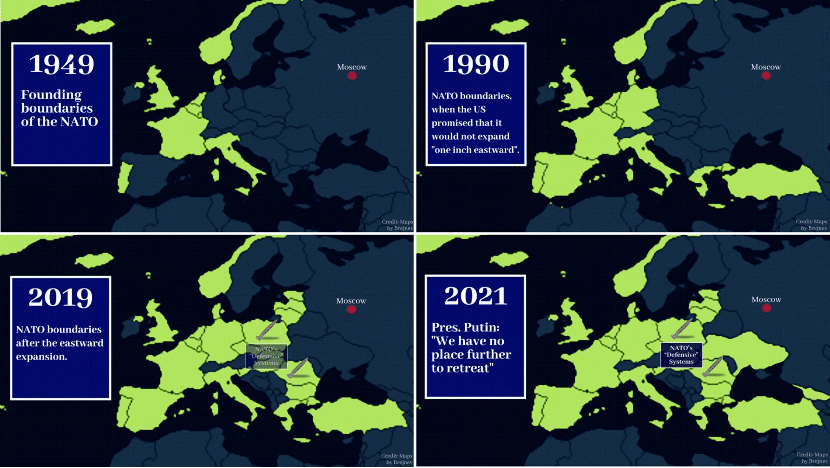
NATO’s Eastward Expansion.


No comments:
Post a Comment